Material Cycles and Waste Management
|
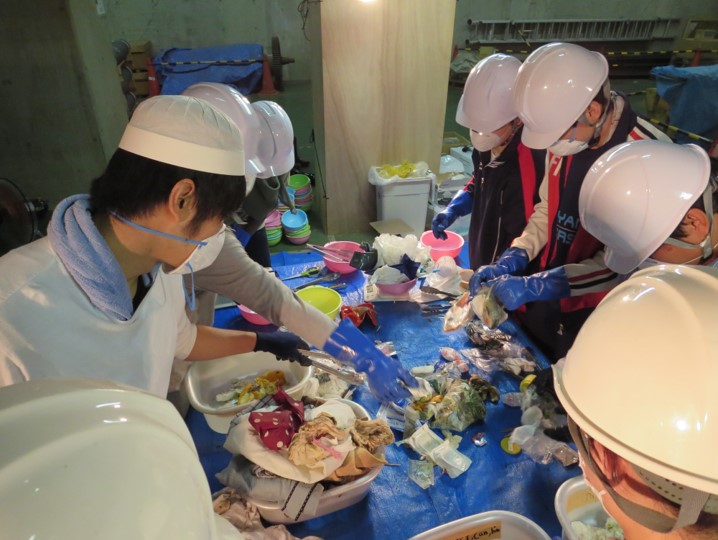
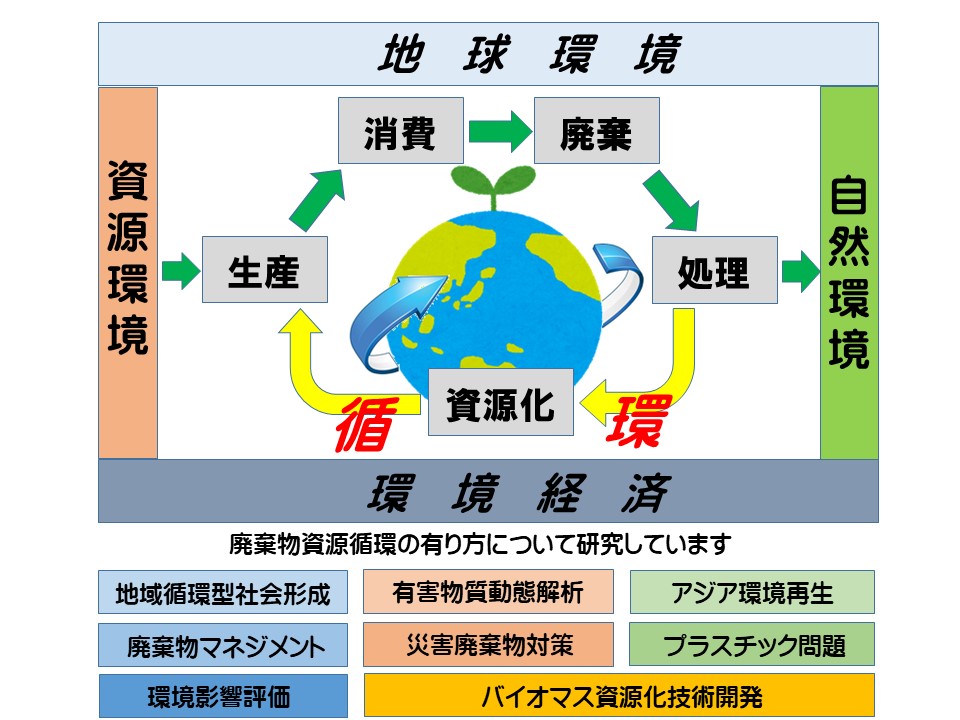
Regional waste material recycling towards low carbon society
Sanitary waste treatment is a fundamental in solidwaste management, moreover, it is required that “fromwaste to material” and “from waste to energy” to mitigategreen house gases emission. Solid waste processes, suchas waste separation at source, segregated waste collection,optimal waste transportation, material and energy recoverytreatment, and safe landfill disposal, should be combinedappropriately so as to shorten the environmental burden.Our laboratory studies on designing methods to establish asophisticated solid waste management that is suitable forsustainable regional society, specially in Asia.
|
Study on the dynamics of mercury emissions under anthropogenic activities for evaluating the effectiveness in the Minamata Convention on Mercury
The Minamata Convention on Mercury (hereinafter referred to as the “Minamata Convention”) was adopted at the initiative of the Japanese government to prevent health and environmental impact caused by mercury and mercury compounds on a global scale. In order to ensure the steady implementation of the Convention, the Parties are required to take measures by combining various technologies and institutions. The evaluation of the effectiveness of these measures must take into account the changes in mercury behavior between the present (after the Convention enters into force) and the past (before the Convention enters into force). The Minamata Convention requires the Conference of the Parties to evaluate the effectiveness of the Convention, and it is expected that Japan will take the initiative in presenting scientific evidence to lead discussions on how to evaluate the effectiveness of the Convention. Currently, it is not yet settled how to evaluate the effectiveness of the Convention; however, it needs to be done by 2023. For this reason, this study is aimed at quantitatively understanding mercury behavior under anthropogenic activities, assessing the environmental impact of anthropogenic mercury emissions from the perspective of life cycle assessment, and quantitatively evaluating future mercury emission reduction scenarios, including the implementation of the Minamata Convention, thereby helping to evaluate the effectiveness of the Convention.