Genetic Engineering
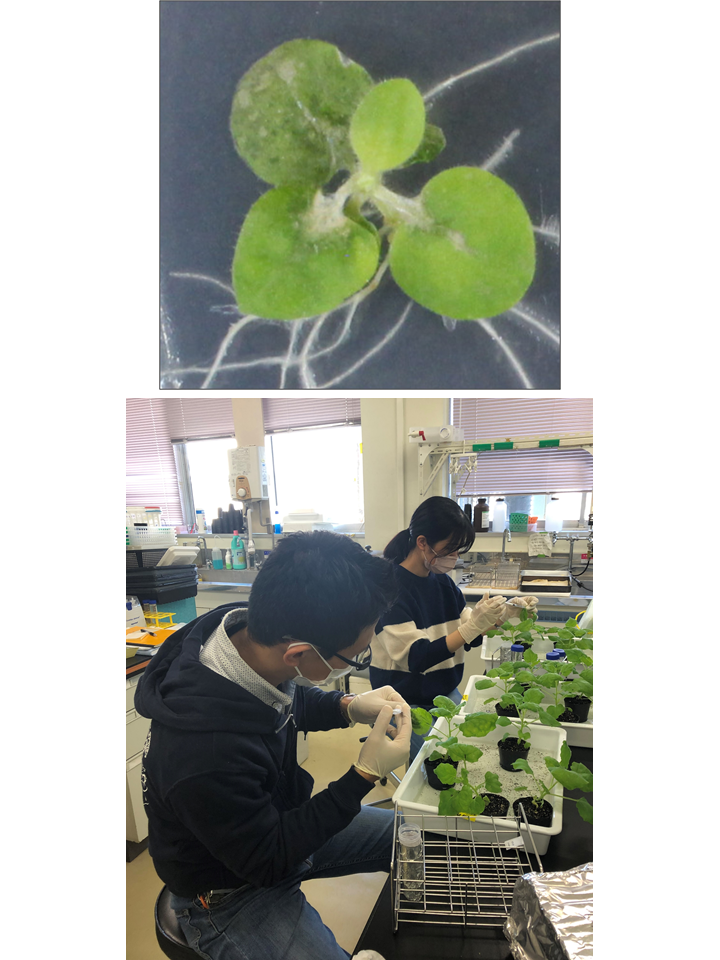
Understanding the pathogenicity of plant pathogens and elucidating plant defense mechanisms against plant pathogens is essential for plant disease control. Our research is focused on elucidating the pathogenicity of plant pathogens and plant resistance mechanisms at the genetic level using molecular genetic methods, with a view to their application in disease control.
 |
|
|---|
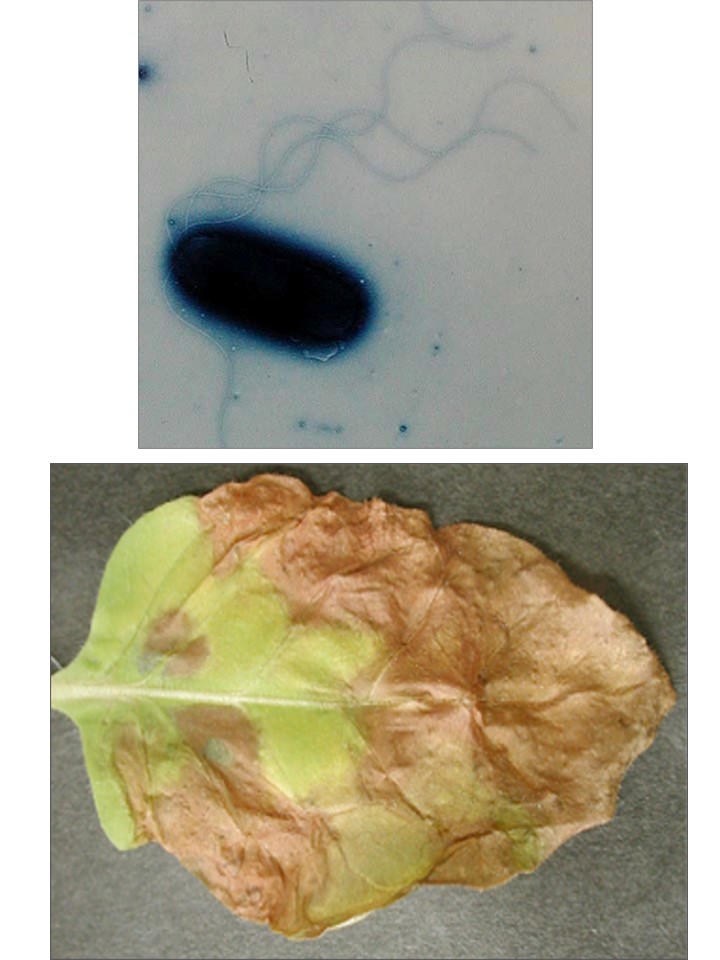
Plant pathogens have evolved various molecular mechanisms to establish infection in host plants. Even among plant pathogenic bacteria capable of infecting host plants, their pathogenicity can vary. Investigating the key molecular mechanisms involved in the expression of pathogenicity in plant pathogenic bacteria can contribute to the development of efficient drug treatments for disease control and the establishment of preventive measures. Currently, we are conducting comparative genomics analysis among multiple strains to explore genetic regions crucial for pathogenicity.
 |
|
|---|
Plant pathogenic bacteria secrete Type III effectors, which act as virulence factors, from a secretion system called the Type III secretion system, suppressing the host’s immune response. Type III effectors exist in diverse families, and many aspects of their target factors and functions remain unknown. We are conducting functional analysis of Type III effectors to gain insights into the infection strategies of plant pathogenic bacteria.
 |
|
|---|
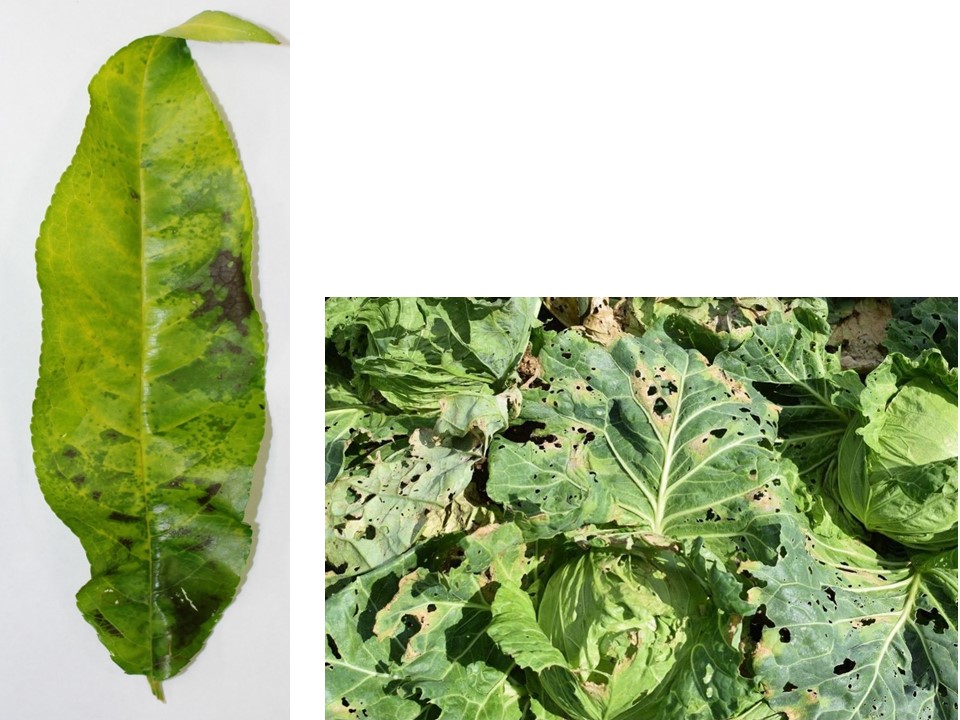

(L): Bacterial canker and spot on peach caused by Xanthomonas (R): Bacterial blight on cabbage caused by Pseudomonas
I aim to elucidate the infection mechanisms of plant pathogenic bacteria, particularly those belonging to the genera Pseudomonas and Xanthomonas. These bacteria cause severe diseases in agriculture, yet their infection mechanisms are not fully understood. Currently, I am focusing on the bacterial spot and canker of stone fruits caused by Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni. I am trying to identify the virulence factors necessary for disease development. I try to develop effective disease control strategies based on molecular infection mechanisms.